Welcome to the March 2022 AI Newsletter from the GovWebworks AI Lab. Our roundup of the latest articles and news relating to artificial intelligence and online services in the public sector touches on important topics in the industry, including:
We hope you find this information as interesting as we do. If so, feel free to share with your colleagues and encourage them to sign up for the AI Newsletter and join the conversation! Or email us at ai@govwebworks.com to talk about using AI to optimize your organization’s digital goals.
#1: Automated Machine Translation facilitates communication with unreached audiences
Key takeaway: Machine translation could fill an especially large gap in services to provide personalized written instructions for non-English speakers.

Despite some current limitations, machine translation can help government agencies customize their communications for non-English speaking audiences. Tools like Google Translate’s api can be integrated directly into content management systems like Drupal and WordPress to enable automated and semi-automated translation of content into multiple languages. This process can be incorporated with workflow processes to allow manual review and editing of the translated content.
Translation services like Google Translate are based on generalized language models, and can have difficulty with domain specific terms. For example, the medical industry. That’s why it’s important to assess how critical the veracity of the translations are for each type of content by assigning each a risk factor.
We recommend creating a translation planning spreadsheet which includes:
- Types of content that will be translated
- Fields that will be translated
- Risk factor – For example, general information about an organization would have a lower risk factor than treatment recommendations for a medical condition.
- Domain specific terms that might be difficult for automated translation to handle
- Risk factor if these are translated incorrectly
Once you have your spreadsheet, you should run some machine translation tests on the identified content to assess the quality of the translations.
For low risk content, “good enough” may be all you need. For content with a high risk factor or domain specific content, you may need to train the language model on custom data.
Services like Google’s Machine Translation API have AutoML features that let you train the translation service on your custom data to improve the results without the need for any custom coding/development.
To learn more about how translation tools can facilitate audience communication, see the article:
Doctors often turn to Google Translate to talk to patients
#2: Use natural language to convert, clean, and modify your data
Key takeaway: Pretty soon you will be able to just talk to your data.
If you’ve ever worked with text file formats such as JSON, CSV, and YAML, you know that it can be tedious to reformat them, convert them into different formats, remove entries, reorder data, etc.
New capabilities in tools like GPT3 allow you to use natural language to automatically reformat and modify data just by telling it what you want using natural language.
For example if you had a CSV file you wanted to convert to JSON format you could just say: “Convert the list to JSON.” Or tell it to “remove the city and state columns.”
These kind of capabilities are available now and can be integrated into existing toolsets via an API from OpenAI. Likely these capabilities will make their way into tools like Excel, VSCode, and others in the near future.
Learn more about AI based data and code manipulation:
#3: Improve support response times and reduce costs by leveraging NLP solutions
Key takeaway: AI can be leveraged to help triage support requests.
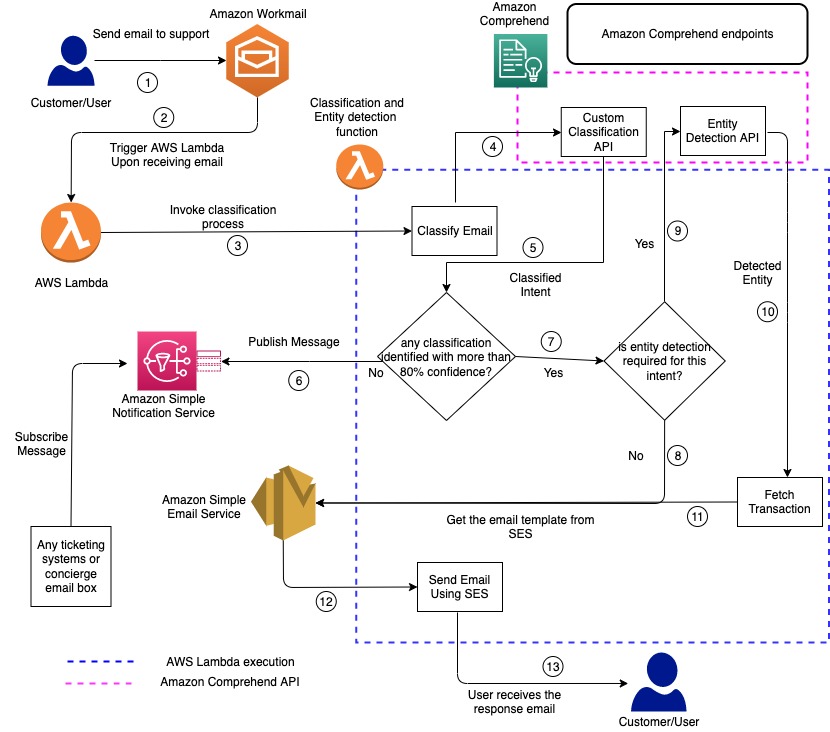
Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools such as AWS Comprehend, Hugging Face, and Google Natural Language can automatically classify support inquiries across multiple channels such as email, webforms, and virtual assistants/chatbots.
Automated workflows can be setup with integrated NLP tools to classify incoming support requests into predefined categories (for example, “Account Login Help”, “Hours of Operation”, etc.). These requests can then be automatically routed to the appropriate internal support channels for review and follow-up.
Learn more about automated email responses:
Learn more
- Sign up for the AI Newsletter for a roundup of the latest AI-related articles and news delivered to your inbox
- Find out more about using AI to optimize your organization’s digital goals